Confronted with quite a few cybersecurity threats and challenges, however missing sufficient cyber coaching, African nations hope to develop the depth of expertise wanted to defend towards attackers in 2024.
In December, for instance, the College of Lagos, the American Enterprise Council in Nigeria, and personal firms launched a Cyber Hub to strengthen the cybersecurity ecosystem in Nigeria and assist prepare younger staff. The hassle is the most recent in a sequence of investments in coaching and increasing the following technology of cybersecurity professionals.
The long-term objectives will not be solely to make Nigeria self-sufficient by way of cybersecurity expertise, but additionally to develop home-grown options to cybersecurity issues, says Victor Odumuyiwa, appearing director of the Nationwide Info Know-how Improvement Company’s ICT Hub and a senior lecturer within the Division of Pc Sciences on the College of Lagos.
Within the subsequent few years, the collaboration’s listing of objectives embrace “capability constructing to fulfill instant cybersecurity wants of the nation, creation of sustainable framework[s] for collaboration and partnership, [and] promotion of joint analysis tasks between tutorial establishments and enterprise entities,” he says.
The Digital Cyber Hub in Nigeria is the most recent effort to give attention to constructing a capability for cybersecurity amongst African nations. In July, the Biden-Harris administration introduced a collaboration with the Cybersafe Basis to develop an Africa-specific effort to coach cybersecurity staff, with a give attention to creating alternatives for girls, as a part of america’ Nationwide Cyber Workforce and Schooling Technique (NCWES).
Discovering methods to coach younger staff is essential in fixing Africa’s cybersecurity — and usually, technical — expertise hole, says Confidence Staveley, co-founder of the Cybersafe Basis.
“We now have a expertise hole, created not as a result of we do not have individuals to coach or people who find themselves not inquisitive about gaining the abilities — we do not have sufficient avenues for them to [acquire] data,” she says. “I imagine Africa has the potential to grow to be the expertise capital, by way of cybersecurity, of the world.”
Africa Goals to Construct Cyber Capability
Preventing that development and enhancing coaching is one in every of Nigeria’s priorities. Whereas attackers are rising extra subtle of their assaults, Nigeria has failed to coach its youth inhabitants with the required expertise to defend the nation’s data methods, says College of Lagos’ Odumuyiwa.
The nation has a “lack of know-how concerning cybersecurity points amongst firms, most of the people, and even sure authorities organizations,” he says. Specifically, the nation has “a deficiency of specialised coaching packages and a scarcity of certified cybersecurity personnel, [as well as] insufficient cooperation on cybersecurity issues with neighboring nations and worldwide organizations.”
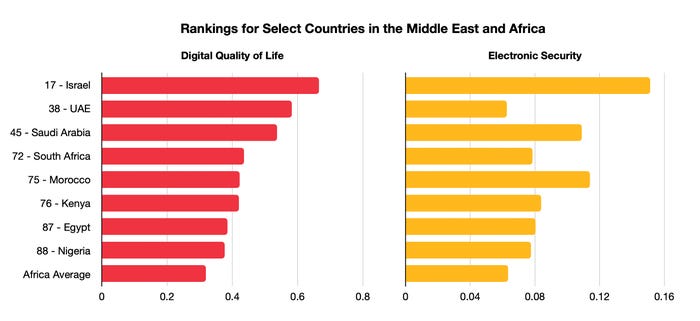
Africa lags the Center East by way of digital high quality of life, however some nations have moved forward in safety. Every nation listed by world rating for DQoL. Supply: Surfshark information
Nigeria, for instance, has seen a major decline in breaches since 2020, however total has a protracted solution to go to strengthen its cybersecurity, rating 88th amongst nations in digital high quality of life and 73rd in digital safety, in accordance with metrics collected by VPN supplier Surfshark.
“Whereas the precise causes for the decline in information breaches will not be identified, stronger privateness legislations and elevated cybersecurity doubtless play a constructive position,” says Agneska Sablovskaja, lead researcher at Surfshark. “In [the e-security] pillar, Nigeria lags behind South Africa (72nd) and Kenya (sixty fifth). Nigeria is unprepared to struggle towards cybercrime, and the nation has very low information safety legal guidelines.”
Morocco, Kenya, Egypt Pushing Ahead in Cyber
Whereas Israel and Saudi Arabia lead in measures of digital safety, sub-Saharan Africa is constructing out its personal cybersecurity initiatives. Morocco, for instance, printed its Nationwide Technique for Info Safety and Digital Belief in 2007, and has solely expanded its lead in cybersecurity on the continent since then, within the face of challenges on account of banking Trojans. Firms, akin to consultancy Deloitte, have partnered with the federal government to advertise coaching and analysis to additional develop expert cybersecurity professionals in Africa, in accordance with the annual Cybersecurity in Morocco report.
Total, cybersecurity is anticipated to be a $3.7 billion market by 2025, however it’s preventing towards losses of $3.5 billion yearly, in accordance with world consultancy Kearney’s Cybersecurity in Africa report.
“As a result of cybersecurity is a repeatedly evolving problem, the area should construct the following wave of cybersecurity capabilities,” the report acknowledged. “This requires cultivating the longer term technology of safety professionals and driving R&D round revolutionary applied sciences that may handle rising and unexpected threats.”
Efforts additionally have to give attention to the retention of cybersecurity staff as soon as educated, the Cybersafe Basis’s Staveley says. She notes that in Nigeria, for instance, there’s a time period known as japa, which suggests leaving the nation for higher alternatives overseas.
“The roles are there, however there is a battle to fill these roles,” she says. “Generally employers are torn between [investing] in expertise, particularly when somebody comes into the office for some time after which leaves.”
Each the governments and personal sector organizations in Africa have to be extra methodical and intentional to create sufficient know-how expertise to serve each native wants and the wants of worldwide society, she says.

