
The infamous North Korean hacking group often known as Lazarus continues to use CVE-2021-44228, aka “Log4Shell,” this time to deploy three beforehand unseen malware households written in DLang.
The brand new malware are two distant entry trojans (RATs) named NineRAT and DLRAT and a malware downloader named BottomLoader.
The D programming language is never seen in cybercrime operations, so Lazarus in all probability selected it for brand spanking new malware improvement to evade detection.
The marketing campaign, which Cisco Talos researchers codenamed “Operation Blacksmith,” began round March 2023 and targets manufacturing, agricultural, and bodily safety firms worldwide.
Operation Blacksmith represents a notable shift in techniques and instruments utilized by Lazarus, serving as yet one more demonstration of the risk group’s ever-shifting techniques.
New malware instruments
The primary malware, NineRAT, is Lazarus’ first of the 2 novel RATs. It makes use of the Telegram API for command and management (C2) communication, together with receiving instructions and exfiltrating information from the breached laptop.
NineRAT incorporates a dropper, which can be answerable for establishing persistence and launching the primary binaries.
The malware helps the next instructions, that are accepted through Telegram:
- data – Collect preliminary details about the contaminated system.
- setmtoken – Set a token worth.
- setbtoken – Set a brand new Bot token.
- setinterval – Set time interval between malware polls to the Telegram channel.
- setsleep – Set a time interval for which the malware ought to sleep/lie dormant.
- improve – Improve to a brand new model of the implant.
- exit – Exit execution of the malware.
- uninstall – Uninstall self from the endpoint.
- sendfile – Ship a file to the C2 server from the contaminated endpoint.
The second malware, DLRAT, is a trojan and downloader that Lazarus can use to introduce extra payloads on an contaminated system.
DLRAT’s first exercise on a tool is to execute hard-coded instructions to gather preliminary system info like OS particulars, community MAC deal with, and many others., and ship it to the C2 server.
The attacker’s server replies with the sufferer’s exterior IP deal with and one of many following instructions for native execution by the malware:
- deleteme – Delete the malware from the system utilizing a BAT file
- obtain – Obtain information from a specified distant location
- rename – Rename information on the contaminated system
- iamsleep – Instruct the malware to enter a dormant state for a set interval
- add – Add information to the C2 server
- showurls – No carried out but
Lastly, Cisco’s analysts found BottomLoader, a malware downloader that fetches and executes payloads from a hardcoded URL utilizing PowerShell whereas additionally establishing persistence from them by modifying the Startup listing.
As well as, BottomLoader gives Lazarus the capability to exfiltrate information from the contaminated system to the C2 server, offering some operational versatility.
Log4Shell assaults
The assaults noticed by Cisco Talos contain leveraging Log4Shell, a essential distant code execution flaw in Log4j, which was found and glued roughly two years in the past but stays a safety drawback.
The targets are publicly dealing with VMWare Horizon servers, which use a weak model of the Log4j logging library, permitting the attackers to carry out distant code execution.
Following the compromise, Lazarus units up a proxy device for persistent entry on the breached server, runs reconnaissance instructions, creates new admin accounts, and deploys credential-stealing instruments like ProcDump and MimiKatz.
Within the second part of the assault, Lazarus deploys the NineRAT on the system, which helps a variety of instructions, as highlighted within the earlier part.
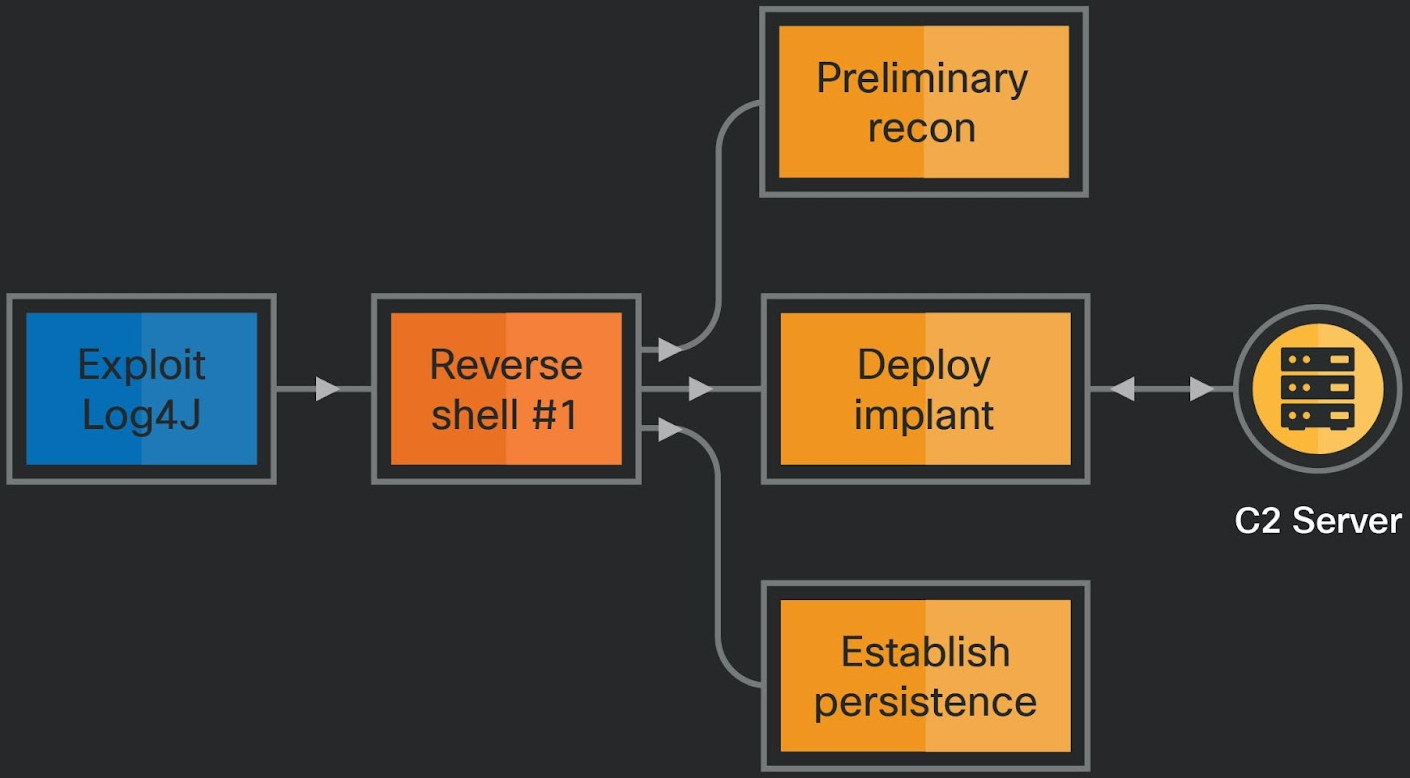
Cisco concludes that it is potential Lazarus feeds different APT (superior persistent risk) teams or clusters underneath its umbrella with knowledge collected by NineRAT.
This assumption is predicated on the truth that NineRAT performs system “re-fingerprinting” in some instances, implying that it might be performing system IDing and knowledge assortment for a number of actors.
